Important RGPV Question
Table of Contents
Toggle
ME-602, Machine Component Design
VI Sem, ME
UNIT 1 – Introduction to Stress in Machine Component
Q.1) What are the primary causes of stress concentration in materials? (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.2) Describe the stress concentration phenomenon in tension, and provide examples. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.3) Explain the S-N Curve and its importance in predicting material fatigue behaviour. (RGPV MAY 2024)
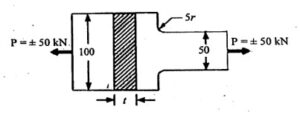
Q.4) A component machined from a plate made of steel 45C8 (S1 = 630 N/mm2) is shown in u1 Fig. It is subjected to a completely reversed axial force of 50 kN. The expected reliability is 90% and the factor of safety is 2. The size factor is 0.85. Determine the plate thickness t for infinite life, if the notch sensitivity factor is 0.8. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.5) A machine component is subjected to a flexural stress which fluctuates between +300 MN/m2 and -150 MN/m2. Determine the value of minimum ultimate strength according to
- Modified Goodman relation
- Soderberg relation.
Take yield strength = 0.55 Ultimate strength; Endurance strength = 0.5 Ultimate strength and Factor of safety = 2.
(RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.6) Determine the force required to punch a hole of 20 mm diameter in a 5 mm thick plate with ultimate shear strength of 250 MPa. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.7) Give some methods of reducing stress concentration. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.8) Explain notch sensitivity. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.9) Explain stress concentration factor. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.10) What are unilateral and bilateral tolerances? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.11) Differentiate between Hardness and Toughness of materials.(RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.12) List some factors that influence machine design. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.13) What is ‘Adaptive design and Optimum design’? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.14) What is meant by stress concentration? How do you like it into consideration in case of a component subjected to dynamic loading? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.15) A cold drawn steel rod of circular cross-section is subjected to a variable bending moment 565 N-m to 1130 N-m as the axial load varies from 4500 N to 13500 Ν. The maximum bending moment occurs at the same instant that the axial load is maximum. Determine the required diameter of the rod for a factor of safety 2. Neglect any stress concentration and column effect. Assume the following values:
Ultimate strength = 550 MPa
Yield strength = 470 MPa
Size factor= 0.85
Surface finish factor = 0.39
Correction factors = 1.0 for bending
= 0.7 for axial load
The endurance limit in reversed bending may be taken as one-half the ultimate strengths. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.16) Write a brief note on Soderberg’s equation and state its application to different types of loadings. (RGPV MAY 2023)
UNIT 2 – Shafts
Q.1) Determine the diameter of a circular rod made of ductile material with a fatigue strength (complete stress reversal), σe = 265 MPa and a tensile yield strength of 350 MPa. The member is subjected to a varying axial load from Wmin=-300 × 103 N to Wmax=700 × 103 N and has a stress concentration factor 1.8. Use factor of safety as 2.0.
(RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.2) Classify keys. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.3) Discuss the forces acting on key. (RGPV MAY 2022).
Q.4) What is difference between rigid and flexible coupling? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.5) Why a hollow shaft has greater strength and stiffness than a solid shaft of equal weight? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.6) Define equivalent twisting moment and equivalent bending moment. State when the two terms are used in design of shafts? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.7) A 45 mm diameter shaft is made of steel with a yield strength of 400 MPa. A parallel key of size 14 mm wide and 9 mm thick made of steel with a steel with a yield strength of 340 MPa is to be used. Find the required length of key, if shaft is loaded to transmit the maximum permissible torque. Use maximum shear stress theory and assume a factor of safety of 2. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.8) Describe with the help of neat sketch, the types of various shaft couplings mentioning the use of each type. (RGPV MAY 2023)
UNIT 3 – Springs
Q.1) The extension springs are in considerably less use than the compression springs. Why? (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.2) Given Parameters:
Load (F): 1000 N
Spring Rate (k): 200 N/mm
Maximum Deflection (): 25 mm
Calculate:
- The required number of active coils for the spring.
- The solid length of the spring.
- The wire diameter required for the spring.
(RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.3) Distinguish between close coiled and open coiled springs. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.4) What is interchangeable manufacturing? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.5) Design a spring for a balance to measure 0 to 1000 N over a scale of length 80 mm. The spring is to be enclosed in a casing of 25 mm diameter. The approximate number of turns is 30. The modules of rigidity is 85 kN/mm². Also calculate the maximum shear stress induced. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.6) What do you understand by overhauling of screw? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.7) What is self locking property of threads and where it is necessary? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.8) Why are square threads preferable to V-threads for power transmission? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.9) Show that the efficiency of self locking screw is less than 50 percent. (RGPV MAY 2023)
UNIT 4 – Brakes & Clutches
Q.1) Consider a heavy-duty industrial clutch designed based on the uniform pressure theory. The clutch has a diameter of 50 cm and is subjected to a varying pressure distribution from the center to the periphery, ranging from 3 MPa at the center to 5 MPa at the periphery. Calculate the total force exerted on the clutch disc due to pressure. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.2) Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of rope, band, and block brakes. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.3) How does the coefficient of friction affect the performance of a rope, band, or block brake system? (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.4) Write a short note on uniform wear theory and uniform pressure theory and give the expression for mean radius in both the cases. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.5) A single plate clutch, effective on both sides, is required to transmit 25 kW at 3000 r.p.m. Determine the outer and inner diameters of frictional surface if the coefficient of friction 0.255 ratio of diameters is 1.25 and the maximum pressure is not to exceed 0.1 N/mm². Also determine the axial thrust to be provided by springs. Assume the theory of uniform wear. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.6) What is Self-energizing brake? When brake become self locking? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.7) In a band and block brake, the band is lined with 14 blocks, each of which subtends an angle of 20° at the drum centre. One end of the hand is attached to the fulcrum of the brake lever and the other to a pin 150 mm from the fulcrum. Find the force required at the end of the lever 1 metre long from the fulcrum give a tongue of 4 kN-m. The diameter of the brake drum is 1 metre and the coefficient of friction between the blocks and the drum is 0.25. (RGPV MAY 2023)

UNIT 5 – Journal Bearing
Q.1) A single row ball bearing carries a radial load of 8 kN and an 5 axial thrust of 3.5 kN. The radial load factor and the axial load factor are given as 0.56 and 1.48 respectively. Desired reliability is 90 percent. The mounting of the bearing is such that the inner ring is stationary. The shaft rotates at 500 rpm and the expected life is 2500 operating hours. Find the dynamic load capacity of the bearing required for the application. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.2) A deep groove ball bearing of basic design no. SKF 6312 has a dynamic load capacity of 81900 N. If this bearing is expected to carry a pure radial load of 37800 N, find the loading ratio and estimate the nominal life of the bearing in millions of revolutions. If the rotational speed of the bearing is 500 rpm, find the bearing life in number of operating hours. Find the reduction in service life when the radial load is increased by 10000 Ν. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.3) Write a note on the dynamic load capacity of a rolling bearing. (RGPV MAY 2024)
Q.4) How are bearings classified ? (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.5) What is a journal bearing? List any two applications. (RGPV MAY 2022)
Q.6) List the important physical characteristics of a good bearing material. And also explain what is bearing characteristic number? (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.7) A footstep bearing supports a shaft of 150 mm diameter which is counter bored at the end with a hole diameter of 50 mm. If the bearing pressure is limited to 0.8N/mm² and the speed is 100 r.p.m. Find: i) The load to be supported ii) The power lost in friction. (RGPV MAY 2023)
Q.8) What are rolling contact bearings? Discuss their advantages over sliding contact bearings. And write a brief note on factors effecting the life of a bearing.
Q.9) A ball bearing subjected to a radial load of 5 kN is expected to have a life of 8000 hours at 1450 r.p.m. with a reliability of 99%. Calculate the dynamic load capacity of the bearing so that it can be selected from the manufacturer’s catalogue based on a reliability of 90%. (RGPV MAY 2023)
— Best of Luck for Exam —
